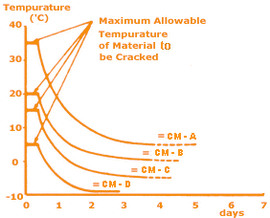
How Does Crackamite Work?
When Crackamite is mixed with an appropriate quantity of water and poured into cylindrical holes drilled in rock or concrete, it hardens and creates an tremendous expansive pressure of 11 MT/m². Crackamite cracks the substrate to be demolished which can then be easily removed with a pick breaker, pneumatic breaker, excavator, etc.
Crackamite develops a very high expansive capability at a consistent volume exceeding 122 Mpa (11,200 T/m²) more than enough to break up any materials to be split or demolished. The tensile strength for most rock is less than 5 - 25 Mpa (500 - 2500 T/m² or 50 - 250 kg/cm²) while reinforced concrete breaks at 3 - 5 Mpa (30 - 50 kg/cm² or 300 - 500 T/m²).
Fracture Mechanism of Crackamite
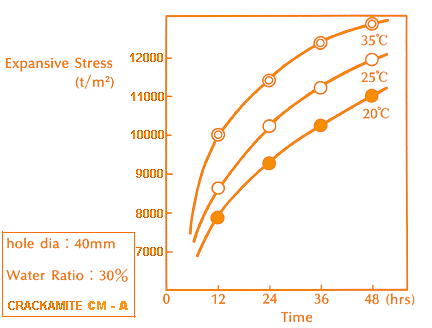
After Crackamite is poured into holes drilled in rocks or concrete, the expansive stress gradually increases with time, and reaches to more than 11,000 T/m² at room temperature after 24 hours. As Crackamite generates its expansive stress, the material to be cracked undergoes a process of (1) crack initiation, (2) crack propagation, (3) the increase of crack width. Therefore, this fracture mechanism is distinguished from a breakage by blasting.
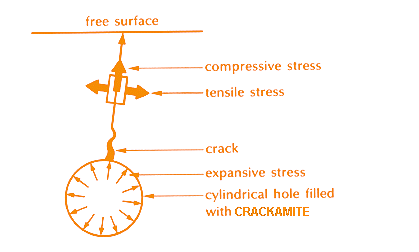
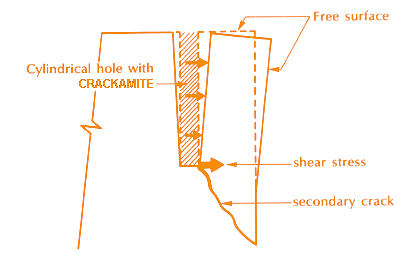
The mechanism by the expansive stress of Crackamite is shown in Fig. 1. Cracks initiate from an inner surface of the hole, being caused by tensile stress at a right angle with the compressive stress that occurs by the expansive stress of Crackamite. The expansive stress of Crackamite continues even after the appearance of cracks, the cracks propagate and also new cracks initiate during the process. Usually, for a single hole, 2 - 4 cracks initiate and propagate. When a free surface exists, the crack, as shown in Fig. 2, is pushed apart mainly by the shear stress, and a secondary crack also arises from the bottom of the hole running toward the free surface.
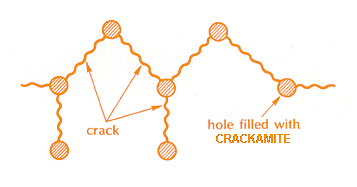
When multiple numbers of holes are filled with Crackamite, that are properly adjacent to each other, the cracks from the hole propagate to connect with the neighbouring holes, as shown in Fig. 3. It is therefore possible to determine the directions of the cracks as planned by appropriately arranging the hole spacing and its depth and its inclination.
stress generated by Crackamite
in material with two free surfaces
adjustment holes due to Crackamite
Establishing Free Surfaces
In the case of trenching, shafting or tunnelling, if all holes are drilled vertically and filled with Crackamite, the crack width cannot increase but horizontal cracks initiate. Therefore, in order to obtain two free surfaces, inclined holes or pre-splitting must be required.
Factors Affecting The Expansive Stress Of Crackamite
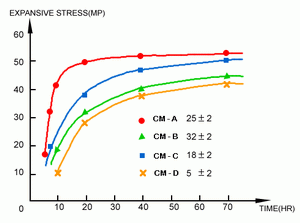
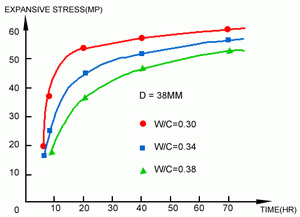
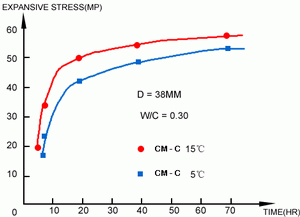
- The expansive stress can be increased to more than 11,200 T/m². (Fig. 1 & 3)
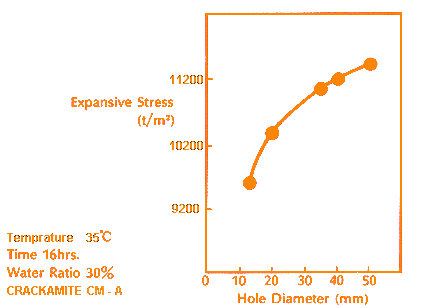
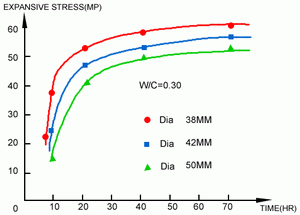
- The larger the hole diameter is, the greater the expansive stress becomes. (Fig. 2)
- There is little change in the expansive stress when the water ratio is in the neighbourhood of approximately 30%. However, the stress is decreased as the water ratio is increased or decreased.